Most of us understand the three tenses Present, Past and Future. However, where a lot of students have trouble is firstly understanding the further divisions within each tense and also transforming a sentence from one tense to the other. Hence today, we are going to look at the easiest way to learn tenses, understand what each tense means and how to rewrite a sentence using another tense.
Types of Tenses
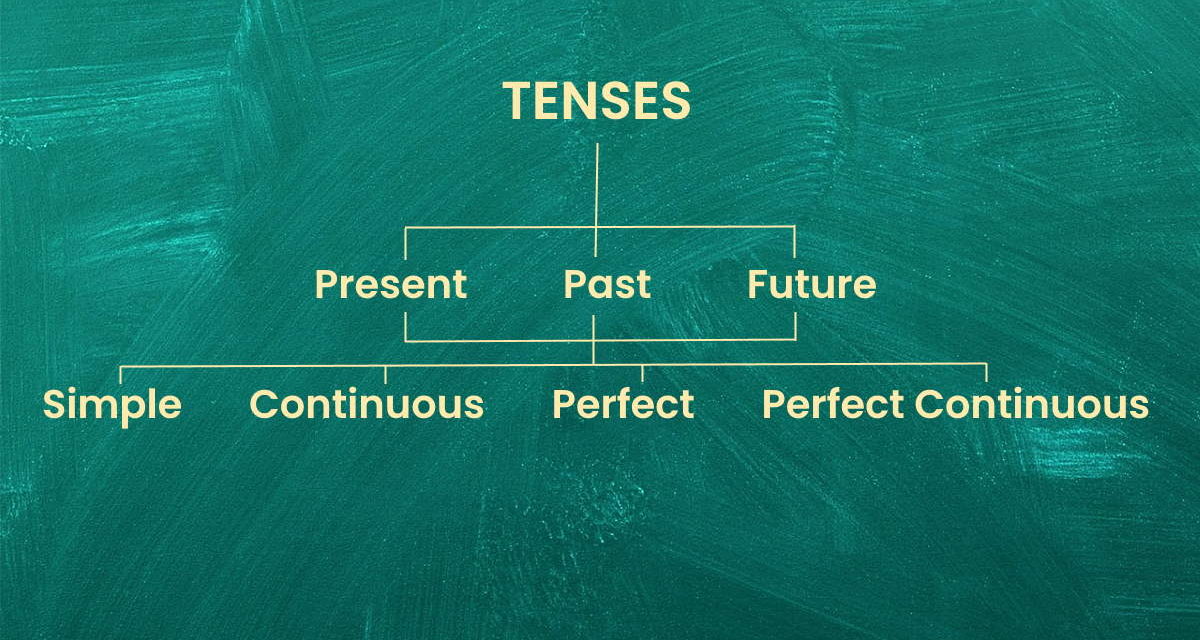
There are three main tenses:
- Present
- Past
- Future
Each Tense is further divided into 4 types:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Hence you can say there are 12 types of tenses in total including the sub-types as follows:
- Simple Present
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Simple Past
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Simple Future
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
Table to Quickly Learn Tenses
Whenever you are confused about tenses, just remember the following table. As long as you remember the given sentences below, you will remember how each tense works.
These tenses are in the same sequence as the 12 types of tenses given above.
- Maya cooks vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya is cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya has cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya has been cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya was cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya had cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya had been cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya will cook vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya will be cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya will have cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
- Maya will have been cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
We shall come back to the above table later. First, let us learn what each tense means.
Meaning of Each Tense
1) Simple Present
Simple Present means any universal truth or a time-table related statement. Universal truth means anything that is a fact and does not change.
Example:
I am a boy.
The sun sets in the west.
She likes to sing.
Examples of Time-Table related sentences:
The train leaves at 5.30 pm every day.
My English class starts at 10 am on Tuesday.
Note: Many students confuse Simple Present as what is happening right now at the moment. However, that is not true. Simple Present is only concerned with universal truths and time-table related sentences.
Also note that in Simple Present, the verb usually is in its second form with ‘s’ or ‘es’ added to it. Such as leaves, starts, likes, sets, goes etc.
2) Present Continuous
Present Continuous is the action that is taking place right now. It is what you are doing at the moment.
Example:
You are reading this article on our website.
I am walking in the garden.
She is exercising in the gym.
Note: In Present Continuous, the verb contains the suffix ‘ing’. Example: walking, running, reading, marching, jumping etc. Also the verb is preceded by a helping verb like are, is, am etc.
3) Present Perfect
Present Perfect means an action that had started in the past but has just got over right now.
Example:
I have finished my homework.
She has completed her practice.
Note: In this tense, the verb is in past participle and preceded by the helping verbs ‘has’ or ‘have’.
4) Present Perfect Continuous
Present Perfect Continuous means an action that had started in the past but is still going on.
Example:
I have been searching for a job since three months.
It has been raining since morning.
Note: In this tense, the verb contains the suffix ‘ing’ and is preceded by ‘has been’ or ‘have been’.
5) Simple Past
Simple Past means any action that has already taken place. It is anything that was done before and is already complete.
Example:
I jumped up and down with joy.
She sang a song
They climbed a high mountain.
Note: In this tense, the verb is mainly followed by the letters ‘ed’ but not always like ‘sang’.
6) Past Continuous
Past Continuous means any action that took place for a period of time before.
Example:
You were reading this article on our website.
I was walking in the garden.
She was exercising in the gym.
Note: In Past Continuous, the verb contains the suffix ‘ing’. Example: walking, running, reading, marching, jumping etc. Also the verb is preceded by a helping verb ‘was’ or ‘were’.
7) Past Perfect
Past Perfect means an action that started in the past and got completed at a point of time in the past itself.
Example:
I had fallen on the ground.
She had waited for three hours.
Note: In this tense, the verb is in past participle form and is preceded by the helping verb ‘had’.
8) Past Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous means an action that had started in the past, went on for a period of time and got over in the past itself.
Example:
We had been waiting at the doctor’s office for 30 minutes.
She had been cooking since morning.
Note: In this tense, the verb contains the suffix ‘ing’ and is preceded by ‘had been’.
9) Simple Future
Simple Future means anything that will take place at a later time or date.
Example:
I will go to the market.
They shall watch a movie in the afternoon.
Note: In this tense, the verb remains in its first form without any changes and is preceded by ‘will’ or ‘shall’.
10) Future Continuous
Future Continuous means any action that will take place at a later time or date and will be going on for a period of time.
Example:
We will be playing in the garden.
They will be coming by evening.
Note: In this tense, the verb contains the suffix ‘ing’ and is preceded by ‘will be’ or ‘shall be’.
11) Future Perfect
Future Perfect means an action that will take place in the future and will be completed at a point of time.
Example:
I will have gone to the fair by now.
The chef will have finished the meal by afternoon.
Note: In this tense, the verb is in the past participle and is preceded by ‘will have’ or sometimes ‘shall have’.
12) Future Perfect Continuous
Future Perfect Continuous means any action that will take place at a later time or date, will go on for a while and get completed in the future itself.
Example:
I will have been looking for a job for so long.
She will have been cooking for all guests at her party.
Note: In this tense, the verb contains the suffix ‘ing’ and is preceded by ‘will have been’.
Also Note: The tenses Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous is rarely used in the English language.
How to transform sentences easily from one tense to the other
To learn how to transform sentences from one tense to the other, we need to come back to our table as follows:
• Maya cooks vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya is cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya has cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya has been cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya was cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya had cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya had been cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya will cook vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya will be cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya will have cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
• Maya will have been cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
Check the underlined words. Those are the only words that usually change when you transform the sentence. Meaning, when we change the tense, we mainly change the helping verb + main verb only in the sentence.
If you notice on the above table, all other words remain the same.
Hence for example, if we say change the following sentence to Past Perfect:
- Maya has been cooking vegetarian food for dinner.
You just need to change “has been cooking” to “had cooked”.
So the final answer would be:
- Maya had cooked vegetarian food for dinner.
So to transform the tense of any sentence, first find the main verb and the helping verb, if any. Then change it as per the tense.
More examples:
1) I ran twenty miles every day (change tense to simple present).
Ans: I run twenty miles every day.
2) We have been searching for you for so long (change to past continuous).
Ans: We were searching for you for so long.
3) Sheila will go to the fair in the evening (change to present perfect continuous).
Ans: Sheila has been going to the fair in the evening.
Did you notice how the sentence remains the same, just the verbs change?
So remember, when transforming a sentence from one tense to the other, follow these steps:
• Locate the main verb + any helping verb before it.
• Remember the table.
• Change the verb + the helping verb as per the tense given.
Few More Examples. Try to convert the tense without looking at the answers first. Answers are given below:
1) She has been living with her brother for a year.
Change to Simple Future Tense
2) I went for a wedding last Wednesday.
Change to Past Perfect Tense
3) The squirrel has climbed the tree as high as it could.
Change to Past Perfect Continuous Tense
4) Father will go to work every day.
Change to Simple Present Tense.
5) The cheetah ran behind the deer for an hour.
Change to Future Continuous Tense.
6) I wish I could visit you soon.
Change to Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Answers:
1) She will live with her brother for a year.
2) I had gone for a wedding last Wednesday.
3) The squirrel had been climbing the tree as high as it could.
4) Father goes to work every day.
5) The cheetah will be running behind the deer for an hour.
6) I have been wishing I could visit you soon.